Black Punk Means Liberation
The present and future of Black punk culture.
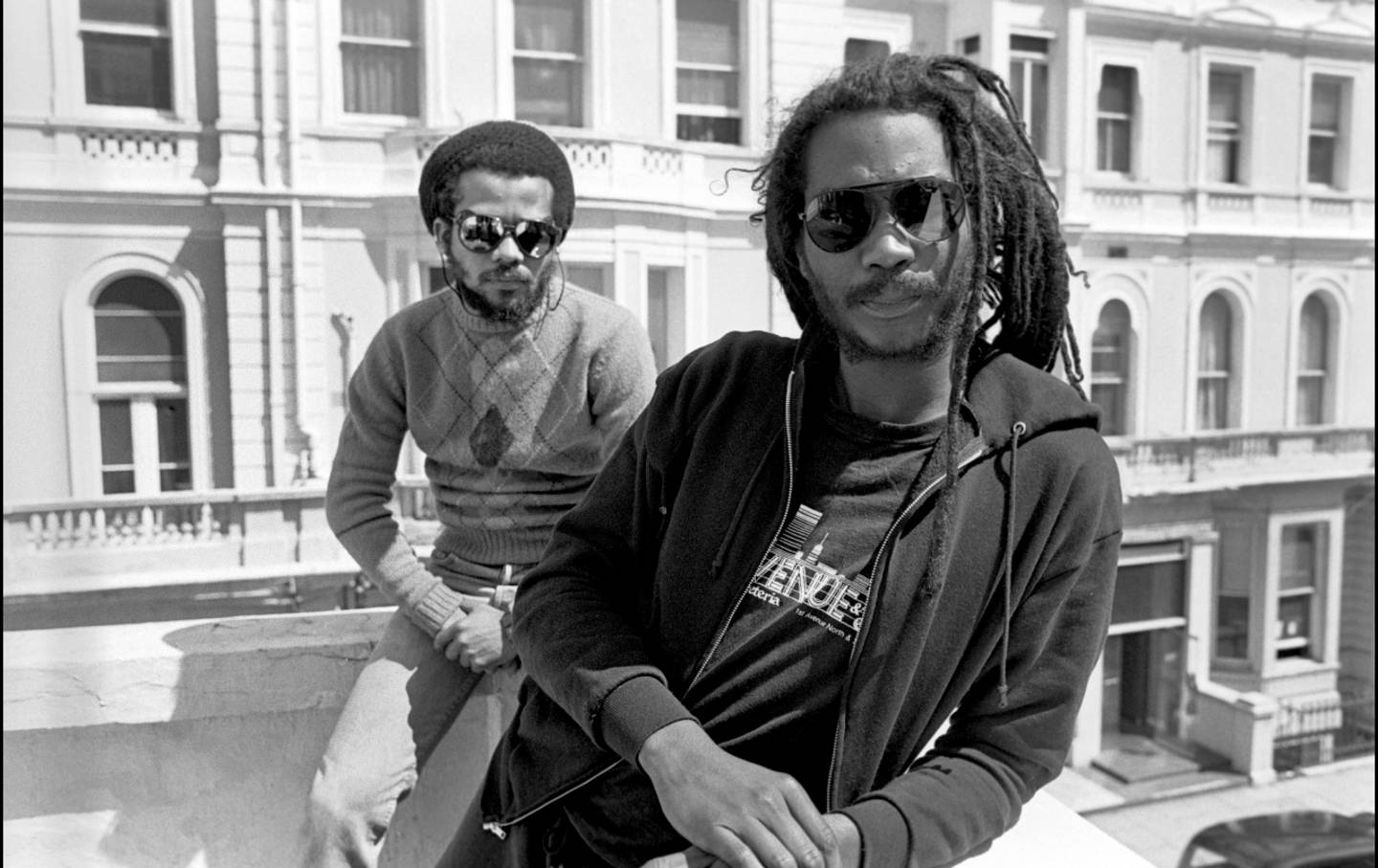

Probably no musical or cultural art form exists in a more contradictory space than punk. When firing on all cylinders, punk is the ultimate anti: Born out of lower- and middle-class white angst in the United States and the UK, punk at its core is about fighting social norms (small and large) and promoting individual expression. Now six decades old, the primarily youth-led form of resistance and counterculture has had numerous highs and lows, including real moments of political resonance, impact, and consciousness-raising. But it has also been diminished by its institutionalization: commercialized, put into museums, and sometimes reduced in relevance to a jingle for some crappy Big Pharma ad on TV.
For this very reason, punk remains a fragile experiment even today. Despite its often lofty aims, it is still subject to the stereotypes and prejudices that society heaps on other minority communities. These vulnerabilities are probed in a worthy new book, Black Punk Now, edited by the graphic novelist and filmmaker James Spooner and the writer Chris L. Terry. Featuring contemporary fiction, nonfiction, illustrations, and comics, Black Punk Now aims to document a lesser-known area of the community and to give punks—especially Black ones—a wider frame of reference for their shared tradition.
Spooner and Terry deserve kudos for their often thought-provoking and richly entertaining volume. But underlying their book, many unanswered questions remain. Few, if any, of the contributions engage with the rise of the far right in the United States, the attack on the US Capitol, police brutality and killings, the emergence of Black Lives Matter, the persistence of Donald Trump, or the continuing battle over abortion rights. Readers are left to wonder if contemporary punks are still raging in a world with so many political and social flash points.
I have been Black all my life, and punk for much of it. Punk subculture has been a part of my existence since I was a teen in the mid-1980s. Boston, my hometown, was an epicenter of the punk/hardcore and college/alternative music scene, and I was all in. The impact of the music, culture, art, and overall DIY ethic and ideology shaped—and still shapes—many aspects of how I view and interact in society. Punk’s radical anti-establishment politics was and remains the most fundamental and valuable part of the movement. The pioneers who believed in the ever-questioning ethos of punk helped me formulate much of the political, cultural, and social work that I do now.
The punk scenes in many major cities were white, male-dominated spaces that replicated the larger culture. But there also was a clear sense of marginalization, isolation, vulnerability, and fluidity that drew other social outcasts and oppressed populations together to create new families. From this shared discontent came a sense of solidarity that continues to influence our politics and social sensibilities. It also sharpened and honed a righteous sense of injustice and a desire to rectify it.
As a young Black punk, existing outside of the mainstream opened me to a new community, new politics, and a greater acceptance of myself. It was these qualities of being a punk that made me feel most at home within this alternative world. Very few subcultures—at least those that I was familiar with—were as vocal about class and class war, environmental justice, reproductive justice, anti-racism, animal rights, the questioning of politicians and mainstream politics, and personal responsibility. Top 40 radio, dependent on rich advertising alliances with Big Business, was certainly not exploring these issues… not with punk’s in-your-face vigor.
Punk, at its best, is not a lifestyle but a life. Not a perfect one, of course, but one that incorporates myriad elements (including music) into a cultural phenomenon that allows for and, in fact, demands the free expression that shatters many preconceived stereotypes and prejudices. This imperative operated in cities across America in the past and came to generally define punk globally. As Dag Nasty, a Washington, D.C., punk band, hollered: “I know I can / I know I will / I know I know what I have to do.” Punk was and remains an obligation.
Black Punk Now is definitively about the present: It is not just about Black punks from the past, but those around today as well. They are here, the book declares, and they want to be heard. Black Punk Now presents a hodgepodge of thoughts, ideas, and angst that runs the gamut in form and content and, as a result, will appeal to a variety of punk and mainstream readers. Although, for some, this might be a weakness of the book, isn’t punk all about variety? As I wrote in my introduction to Craig O’Hara’s 1999 book, The Philosophy of Punk: More Than Noise: “The major problem with trying to explain punk is that it is not something that fits neatly into a box or categories. Not surprising as punk had made the explicit aim of trying to destroy all boxes and labels…. Punk and punk music cannot be pigeonholed to some spiked-haired white male wearing a leather jacket with a thousand metal spikes listening to music real loud.”
Spooner and Terry refuse to pigeonhole punk because they are so familiar with its more diverse and multicultural elements. Spooner, who directed and coproduced the groundbreaking and eye-opening 2003 documentary film Afro-Punk, has long been interested in the contradictory and multifarious nature of punk identity. As Terry says, “A goal of Black Punk Now is to give punks—especially the Black ones—a wider frame of reference; to show all of the strains, styles, and identities of Black punk that are thriving; and give newcomers to the scene more chances to see themselves.”
One of the more illuminating chapters in Black Punk Now asks, “What adjectives would you use to describe Black punk?” The answers from femme organizers of new Black and brown punk festivals reflect a continued awareness that defining yourself is key. Courtney Long, from #BLKGRLSWURLD: “Oh, I would say magical. I just think it’s cool; all the different ideas people come up with when there’s no boundaries. When there’s no box.” Monika Estrella Negra, from the Black and Brown Punk Collective: “Transformative. Black punks have been the blueprint for fusing music and art with political praxis.” Stephanie Phillips, from Decolonise Fest: “Revolutionary. Growing up as a Black girl in the UK, society’s idea for you and what you should be is very limited. And punk in itself is something where you can be whatever you want to be and break free from any constraints.”
While mainstream culture often sees punk as primarily a musical phenomenon, Black Punk Now is careful to show not only the varieties of punk identity but also its genres and modes of expression. Black Punk Now is not just a book about music; it is about how punk as a subculture, and Black punk as a subculture within a subculture, can be an incubator for radical ideas and forms of expression of which music is only one small (though loud) sliver. “Being Black and punk challenges the idea of what people think ‘Black’ is supposed to be…and that is soooooo punk!” writes Bobby Hackney Jr. in his contribution to the book, which discusses his family legacy of punk. It is also a reminder of how African Americans have been involved in the history of rock and roll since its inception but have seldom been acknowledged for their breakthroughs and contributions to the art form.
Hackney’s father and uncles were the founding members of Death, the seminal proto-punk band from Detroit. Death was boldly ahead of its time: Imagine Black punkers competing in the age of Motown with its smooth moves, supple lyrics, and cool threads. The band was formed several years before the amazingly influential all-Black punk/hardcore group Bad Brains roared out of Washington, D.C., and New York.
Popular
“swipe left below to view more authors”Swipe →But Death also sits squarely within the larger history of Black punk. Through the band, one can appreciate the acts of punk resistance that followed, but also the brazen resistance of its own work. Hackney writes that
if you’re doing something that other people don’t understand and you still decide to do it, that’s punk to me. My dad and uncles did this thing that they thought was awesome. A lot of people around them didn’t think it was awesome, but they still did it anyway. They created something out of nothing and found a way to make things happen on their own.
Many of the other contributions to Black Punk Now also examine the themes of striking out on one’s own—of self-mastery and radical acts of creative expression. Some of the contributions also explore how American society as a whole was often not prepared for Black punk culture, let alone punk culture writ large. In a short piece of fiction by Monika Estrella Negra, we are presented with the story of a young Black punk queer woman who leaves Chicago and moves into a gentrifying neighborhood in West Philadelphia. Guilt and displacement, as much as creativity and liberation, are major elements of the story, which sees its main character, Mya, struggle with her identities as Black, punk, and a recent Midwestern transplant now living in a traditional Black community inundated with young white punks, extensive recreational drug use, and hipster outsiders. After drinking at a traditional neighborhood dive frequented by longtime residents, Mya stumbles onto those that are now frequented by new and mostly white punk arrivals. Neither feels entirely like her home or community. “The alienation of being a Black queer woman in a subculture that would never understand her” would come to haunt Mya, Negra writes. “A circle that would treat her presence as a token accessory to cover their insecurity. A privilege that they tried to escape. Expendable. Exotic.”
But even when Black punks struggle to find their place within both the punk and Black communities, their determination to juggle a juxtaposition of identities and loyalties only makes them all that more punk. As Joanna Davis-McElligatt writes in her contribution: “Black punk means liberation, it means doing things for myself, it means family, it means joy, it means healthy rage, it means radical self-acceptance. Black people plus punk rock equals me.”
More from The Nation
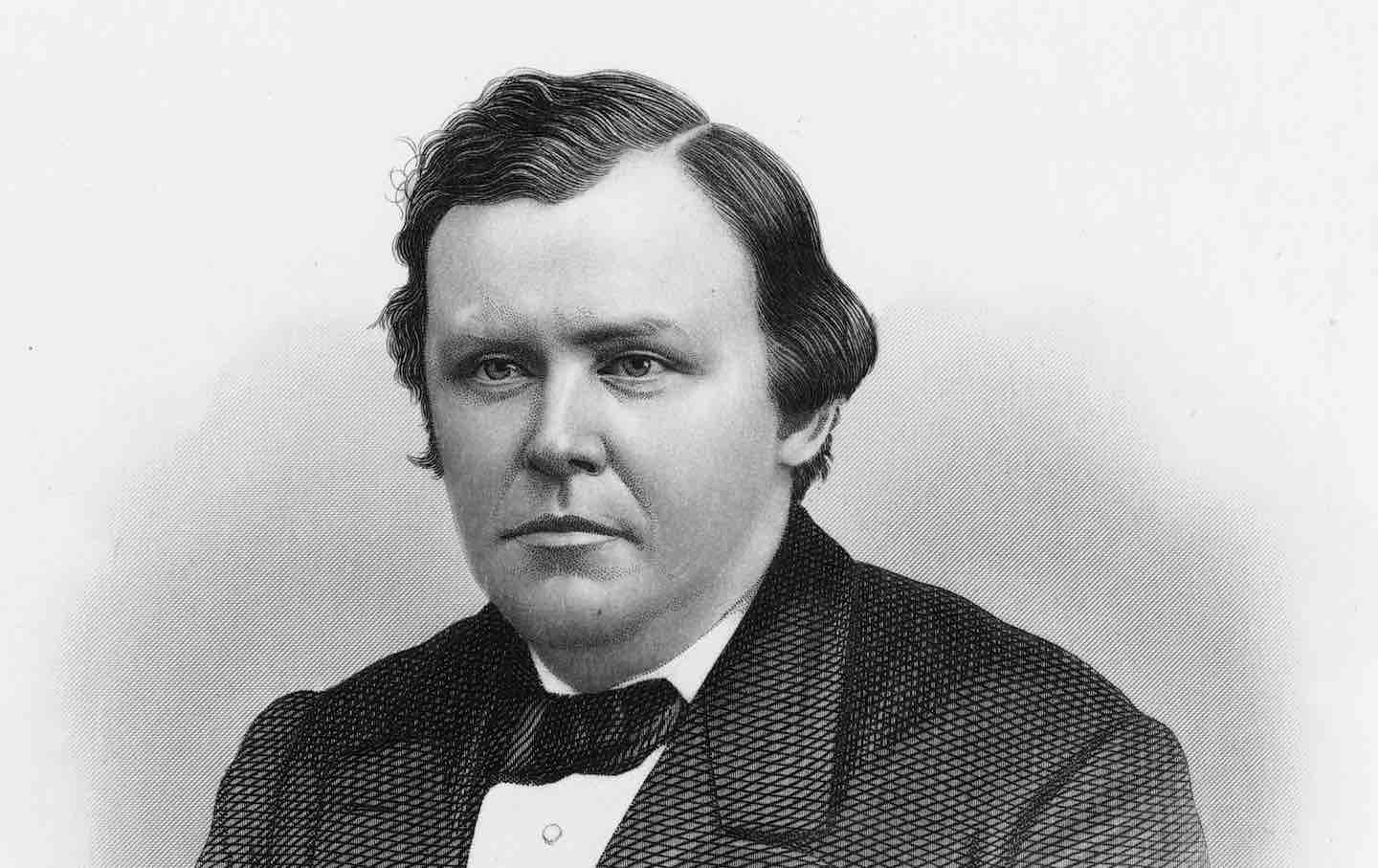

The Peculiar Case of Ignatius Donnelly The Peculiar Case of Ignatius Donnelly
The Minnesota politician presents a riddle for historians. He was a beloved populist but also a crackpot conspiracist. Were his politics tainted by his strange beliefs?
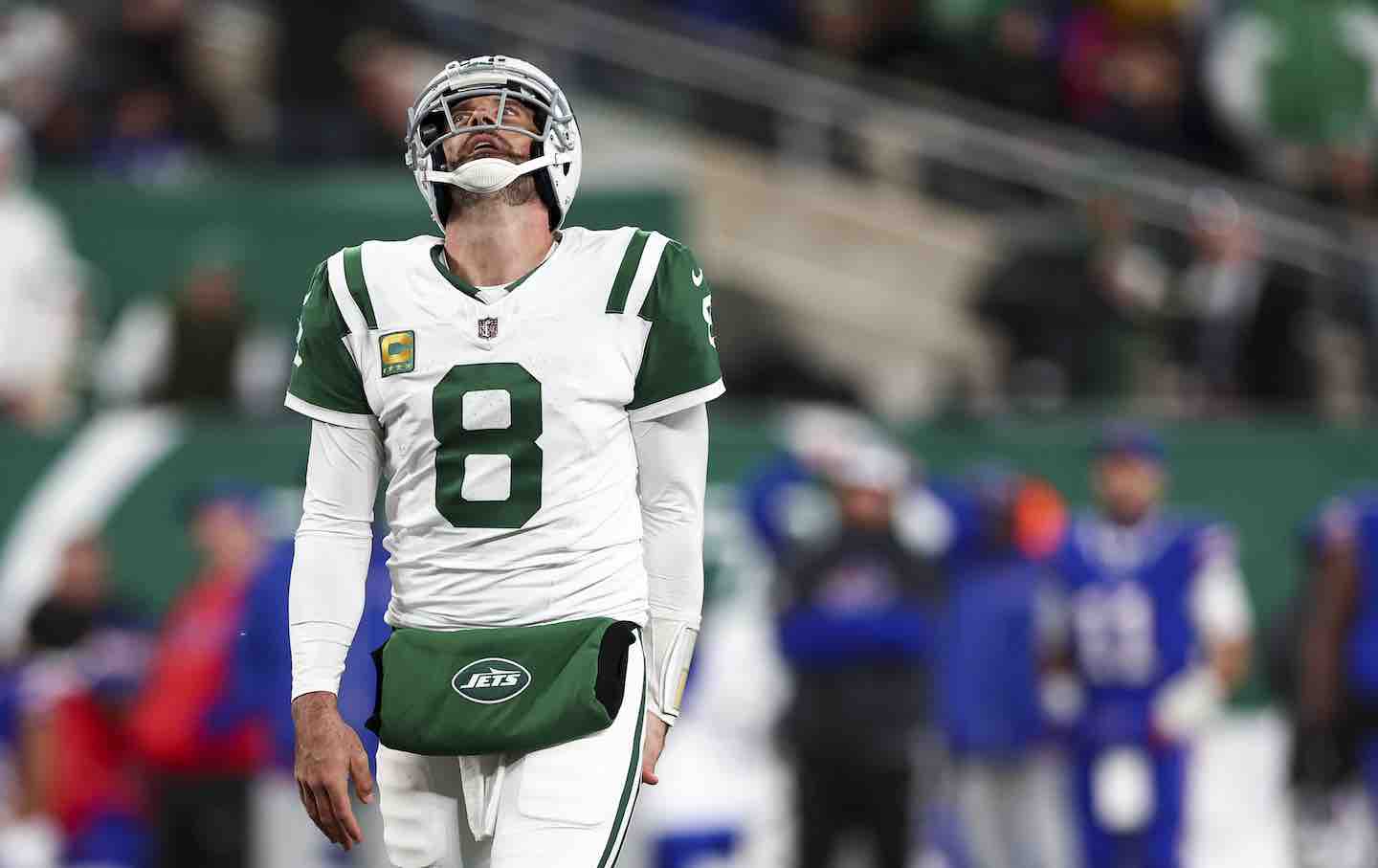

The Agony of Aaron Rodgers The Agony of Aaron Rodgers
Is he the world’s most interesting athlete or is he just a washed-up crackpot?
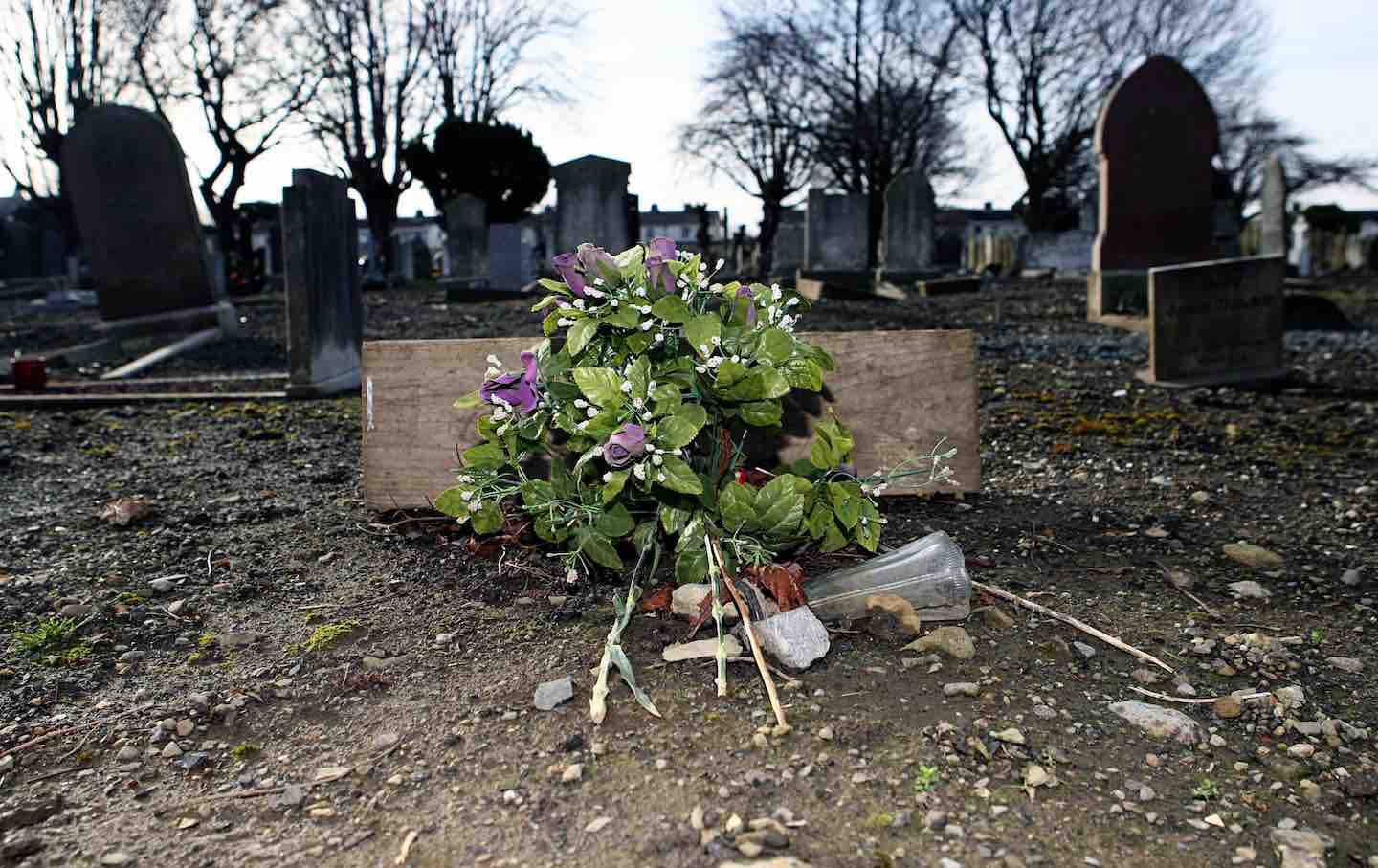

Can You Understand Ireland Through One Family’s Terrible Secret? Can You Understand Ireland Through One Family’s Terrible Secret?
In Missing Persons, Clair Wills's intimate story of institutionalized Irish women and children, shows how a family's history and a nation’s history run in parallel.
Peter Schjeldahl’s Pleasure Principle Peter Schjeldahl’s Pleasure Principle
His art criticism fixated on the narcissism of the entire enterprise. But over six decades, his work proved that a critic could be an artist too.

How the Western Literary Canon Made the World Worse How the Western Literary Canon Made the World Worse
A talk with Dionne Brand about her recent book, Salvage, which looks at how the classic texts of Anglo-American fiction helped abet the crimes of capitalism, colonialism, and more...

Along the Roads That Built Modern Brazil Along the Roads That Built Modern Brazil
José Henrique Bortoluci's What Is Mine tells the story of his country’s laborers, like his father, who built its infrastructure, and in turn its fractious politics.


