Beyond the Visible
Nuri Bilge Ceylan’s About Dry Grasses.
The Genius of Nuri Bilge Ceylan
About Dry Grasses is long, dense, elliptical—and brilliant.
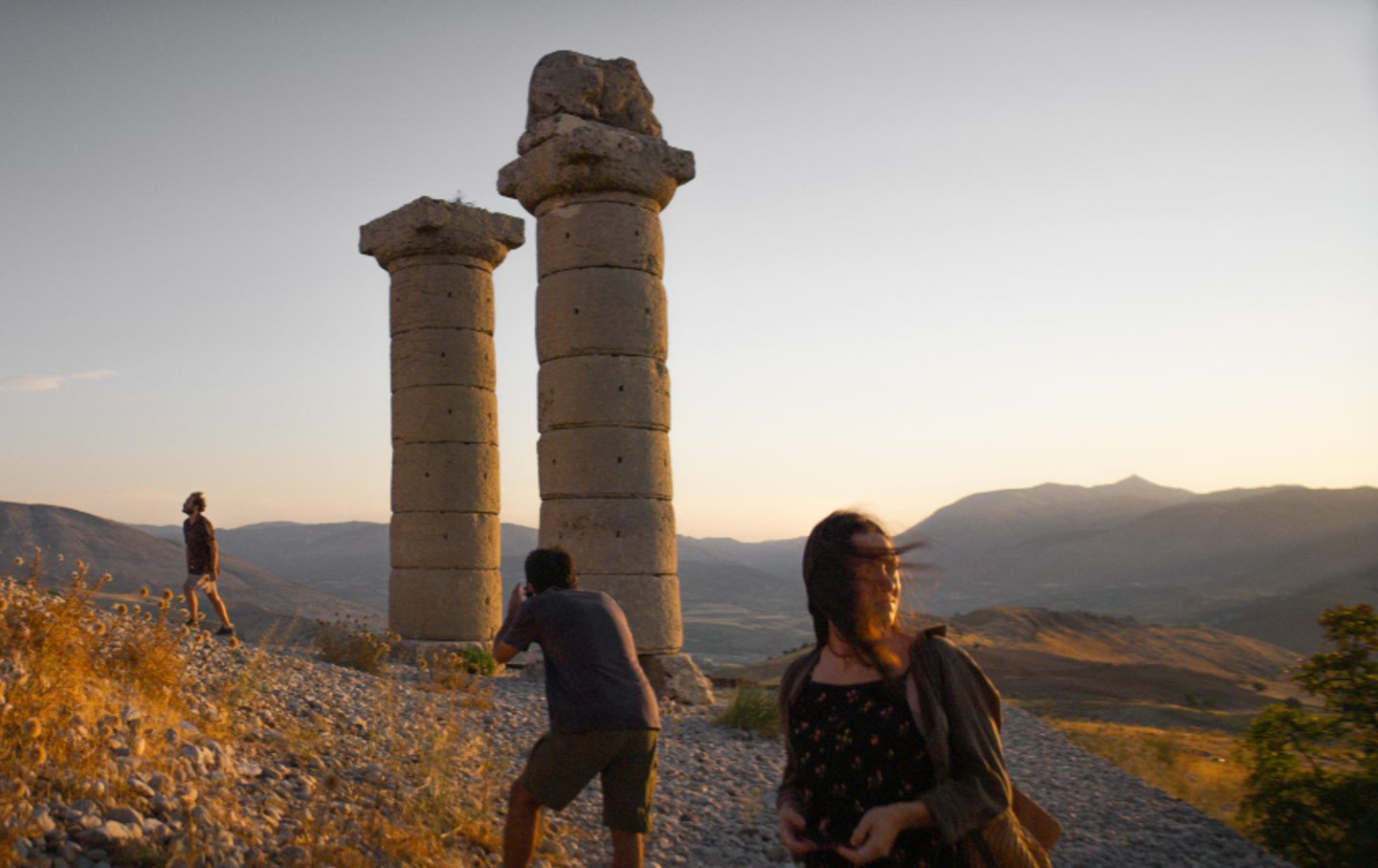

A scene from About Dry Grasses.
The sounds of harsh weather over a black screen, then a snowy landscape in long shot. A white van drives into the frame, the red triangle of a yield sign the one note of color here, and a man gets out. He walks alone toward the camera. As About Dry Grasses begins, the only clear thing is that we are in the land of Nuri Bilge Ceylan, the Turkish filmmaker who, over the course of nine films, has carved this particular terrain out of rural stagnation and urban anomie.
Long, dense, and elliptical, Ceylan’s films are thorny and difficult, and rousing in their starkness. There is a great pleasure in seeing them, despite their bitter stories of failure and regret. Each one, from The Small Town (1997) to The Wild Pear Tree (2018), records something essential. On a basic level, Ceylan’s movies are a place where, in the future, we will see snow photographed in color once there isn’t any snow (or only computer-generated snow in movies). They will be a way that we remember the reality of the world that once was.
Another example: About Dry Grasses ends with scenes shot in and around the ruins of the Karakuş Tumulus, a grand funerary monument featuring columns topped with sculptures—including a monolithic version of the statuette in The Maltese Falcon. In the short time since Ceylan shot those scenes, one of the pillars, over 2,000 years old, has collapsed—another casualty of the Turkey-Syria earthquakes that claimed tens of thousands of lives a year ago and that much of the world has already forgotten. Ceylan’s films recognize this moment of ours, in which things fade from memory too quickly.
At the center of About Dry Grasses is the story of Samet (Deniz Celiloğlu), which Ceylan tells with a certain eternal gaze. At first Samet seems to be the kind of guy who gets along with everybody: He lives in a remote part of eastern Turkey—Ceylan country—where the government has assigned him his job as a middle-school art teacher He’s chummy with a wide range of characters: the local veterinarian, the military police sergeant who randomly checks people’s IDs, even a wannabe Kurdish guerrilla. Samet has also become quite buddy-buddy with Sevim (Ece Bağcı), the prettiest, liveliest girl in his class, calling on her more than the other students and walking arm in arm with her down the school’s corridor.
Here we have a problem, and not just with Samet’s behavior. By the time his inappropriate conduct with Sevim blows up in his face, About Dry Grasses still has 150 minutes to go. Ceylan’s last two films were also three hours and 15 minutes long—this now seems to be his preferred length—and that is a lot of time for things to get worse for Samet, who, in the film’s first 45 minutes, has been slowly revealed as a disgruntled snob. Samet, we come to understand, exists in the ultimate condition of the Ceylan protagonist: He longs to be in Istanbul instead of living on the edge of nowhere, and his pining for the city is coupled with an unwillingness to commit to or even recognize anything that might help him get there.
But as we watch About Dry Grasses, we realize that the film’s running time also opens it up in many other ways. In fact, its length allows Ceylan to keep changing the stakes. As Samet continues doing the wrong thing, Ceylan deepens the film’s politics, subtly placing his story in the context of suicide bombings and Kurdish resistance, a world in which Samet’s complaints about his lot in life are trivial and petty.
A non-feel-good movie, set in the present, about the impossibility of change and the opacity of human relations, About Dry Grasses is The Holdovers in reverse, its opposite in every way. It takes place right after winter break, not during, as if it were picking up where The Holdovers left off, and it’s about a teacher who does not lose his job but probably should. It also comes last in a sequence of three recent movies about teachers and students; in between The Holdovers and About Dry Grasses was The Teachers’ Lounge, an Oscar-nominated German film by a Turkish German director, İlker Çatak, that shares a scene with Ceylan’s, of students being unfairly searched in class by school administrators. It’s almost as if the cinema were trying to get to About Dry Grasses but had to go through a metamorphosis first, arriving there in stages. As François Truffaut once noted, “If three films come out in Paris in the same month, and all are set in the same period—for example, the Occupation—or in the same place—Saint Tropez—woe to the one that follows the first two, even if it is the best of the lot.”
About Dry Grasses is the best of the lot. I liked The Holdovers and thought The Teachers’ Lounge was OK, but here we are dealing with the best the cinema can offer. It’s a brutal fact that Truffaut was right: When it comes to the box office, the third time is not the charm. Few American moviegoers have even heard of About Dry Grasses. The time of “slow cinema” may be passing, and although Ceylan’s films are not that—not quite—it is easy to conflate what he does with the kind of festival movie that values length over acting and screenwriting, over drama.
And I do mean “drama.” Ceylan’s 2014 film Winter Sleep was built on Chekhov, and his other films often adhere to 19th-century dramatic and literary forms while remaining resolute in their cinematic modernity, much in the way that Ingmar Bergman’s and Andrei Tarkovsky’s films did. Those auteurs are two of Ceylan’s avowed masters, and I think it’s time to admit that he has equaled or surpassed them, even though saying so won’t matter, or will seem perverse to the generation that came of age in Bergman’s heyday and irrelevant to the current generation, split as it is between pseudo-obsessional pop culture and radical fragmentation.
Ceylan is out of step with popular culture in other ways too. His radicalism is subtle. One aspect of that is how Sevim’s story eventually becomes a subplot in About Dry Grasses as Nuray (Merve Dizdar), a teacher with a prosthetic leg, takes over as the film’s female lead. Nuray splits her time between Samet and his work colleague and roommate, Kenan (Musab Ekici), another man in that other constant Ceylanian state, bachelorhood. Dizdar won the Best Actress award at Cannes last year for her performance (to the revulsion of much of the Turkish establishment), probably because of the film’s long centerpiece scene, a conversation between Nuray and Samet in her apartment that begins with her excoriating his politics and ends in one of the most caddish seductions in movies.
The scene has great emotional power, building menace in a slow burn, before breaking at the height of its tension when Samet leaves for the bathroom to pop a pill. At that point, Ceylan does something totally unexpected, and yet after that scene, which would end most movies, we still have 45 minutes to go. Similarly, Ceylan has become so supple with what he does that in About Dry Grasses he can introduce a gun, in a shot with a great deal of force and implied future violence, and then let all that dissipate into mystery, violating the Chekhovian diktat on purpose.
About Dry Grasses becomes a Jules and Jim for the provinces far from the center of empire, as in a Kafka parable, and it’s equally far from the golden age of the European art film. Ceylan is part of a generation of great filmmakers who do well at festivals and whose films get limited theatrical releases in the United States, but who, in their own time, are denied the status of their forebears. That’s because the cinema itself is moving to the edges. The group that Ceylan is arguably a part of includes Jia Zhangke in China, with his similar focus on those lost on the periphery; Lucrecia Martel in Argentina; Lee Chang-dong in South Korea; Carlos Reygadas in Mexico; and all your major Romanians.
In a press statement, Ceylan mentioned that he wanted to show in About Dry Grasses three things that are, as the wannabe guerrilla says in the film, “beyond the visible”—an area hard to put on the screen. Those things are “how ideals can in time turn into disappointments”; “the burden of occupying a point in time”; and “the feeling of nothingness impossible to shake.” The film’s long coda, set in the summer, explains its title and brings those themes to the fore, introducing a voice-over narration from Samet for the first time.
Popular
“swipe left below to view more authors”Swipe →Yet what is said is less important than what we see. As Samet, Nuray, and Kenan wander among the ruins, this film ends the way another French film, Les Enfants Terribles, began: with a snowball fight recalled in flashback and voice-over. In the Melville and Cocteau film, the schoolkids are interrupted by an adult—but here the adult is more of a participant than a voice of authority, and the schoolkids are girls, not boys. As Samet drones on about the hopelessness of his life, Sevim and the other girls are blissfully cut off from hearing him. They pelt him with snow, deaf to his misery as well as his earlier outbursts—including one in which he yelled at them that they could study art all they want but they would still end up being nothing but potato and beet farmers because “the show must go on.”
“The puzzling incident deeply distressed the principal,” Cocteau says in the narration during Les Enfants Terribles’ schoolboy scene. In Ceylan’s film, Samet, adrift in the crumbling remains of an ancient kingdom, becomes like the lost Odysseus: “The storm winds have snatched him away into obscurity. He is gone beyond sight, beyond knowledge.” We are left to remember him by his dialogue earlier in the film, when he was trying to seduce Nuray, pretending to self-knowledge by implying that he had lied to Kenan to get her alone. “Have I been an asshole?” he asks, even though he knows the answer.
More from The Nation

What Comes After the Apocalypse? A Q&A With Joshua Oppenheimer What Comes After the Apocalypse? A Q&A With Joshua Oppenheimer
Oppenheimer’s latest film, The End, is a Golden Age, postapocalyptic musical crying out from the depths of the earth.

The Peculiar Case of Ignatius Donnelly The Peculiar Case of Ignatius Donnelly
The Minnesota politician presents a riddle for historians. He was a beloved populist but also a crackpot conspiracist. Were his politics tainted by his strange beliefs?

The Agony of Aaron Rodgers The Agony of Aaron Rodgers
Is he the world’s most interesting athlete or is he just a washed-up crackpot?

Can You Understand Ireland Through One Family’s Terrible Secret? Can You Understand Ireland Through One Family’s Terrible Secret?
In Missing Persons, Clair Wills's intimate story of institutionalized Irish women and children, shows how a family's history and a nation’s history run in parallel.
Peter Schjeldahl’s Pleasure Principle Peter Schjeldahl’s Pleasure Principle
His art criticism fixated on the narcissism of the entire enterprise. But over six decades, his work proved that a critic could be an artist too.

How the Western Literary Canon Made the World Worse How the Western Literary Canon Made the World Worse
A talk with Dionne Brand about her recent book, Salvage, which looks at how the classic texts of Anglo-American fiction helped abet the crimes of capitalism, colonialism, and more...


