Striking Workers Cheer Senator John Fetterman’s SNAP Benefits Bill
The proposed law would restore eligibility for federal food aid taken away by Ronald Reagan.

Going on strike can be stressful—especially when you have to worry about how you’re going to feed your family. On Thursday, Senator John Fetterman (D-Pa.) and other progressive lawmakers moved to take some of that pressure off thousands of American workers who are currently on strike by introducing the Food Secure Strikers Act, a bill that would make them eligible for Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits—formerly known as food stamps.
The legislation, sponsored by Fetterman in the Senate and Representatives Greg Casar and Alma Adams on the House side, would modify the existing Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to include language that affirmatively protects the ability of striking workers to receive SNAP benefits, clarify that income-eligible households are eligible for benefits regardless if a member is on strike or not, and protect eligibility for public sector workers who are fired for striking.
The bill faces an uphill battle to passage, with Republicans in control of the House and Democrats commanding a slim majority in the Senate. The PRO Act, a far more sweeping piece of legislation to boost unionization, was unable to secure a filibuster-proof majority when Democrats held both chambers of Congress in 2021 and 2022. The GOP-controlled House has made clear that it aims to defang federal labor law, not bolster it.
When asked about the legislation’s chances of coming up for a vote and becoming law, Casar struck an optimistic tone: “I’m always hopeful, we have to be. If just a handful of Republicans decided to stand up for the rights of their constituents, we could bring this—and so many other bills—to the floor.”
But despite the tough political environment, rank and file members of SAG AFTRA, one of the unions currently on strike, cheered the move, calling it a step in the right direction.
“Helping actors feed themselves—I don’t know who would be against that,” said Ryan Wick, a D.C.-based actor and rank-and-file SAG-AFTRA member. “I think it’s great. Any money people can save on food, they can put towards rent,” he told The Nation, evoking the dire financial straits of many working actors.
Over 85 percent of SAG-AFTRA do not earn enough to qualify for union health insurance, which is only $26,470 a year. And while SAG-AFTRA is able to offer some support to members currently on strike through its Emergency Financial Assistance and Disaster Relief Fund, members must apply and show “immediate financial need” in order to tap into it.
Elliot Bales, a SAG AFTRA member and actor based in Virginia echoed Wick’s comments, saying SNAP benefits would be a boost for many actors in the community, “especially the most vulnerable parts of our population.”
Wick and Bales are two of 160,000 unionized actors currently on strike to demand better working conditions, new compensation structures, and job protections from AI. They’re joined on the picket line by 11,500 screenwriters with the Writers Guild of America who have been on strike since early May. Together, the two strikes have effectively made Hollywood grind to a halt in a show of force not seen since 1960.
This summer’s high-profile labor activity is not confined to show business. On Tuesday, UPS and the Teamsters came to a tentative deal, narrowly averting an August 1 strike that would have seen 340,000 Teamsters-represented workers walk off the job. The deal now goes to a vote by union members. Meanwhile, the United Auto Workers kicked off negotiations with the Detroit Three automakers in July. The current UAW contract expires in mid September—and if the companies and UAW do not negotiate a new one, some 150,000 UAW represented workers will walk off the job.
The sponsors of the Food Secure Strikers Act made clear that the bill is a direct response to the strike actions happening around the country. “It’s a hot labor summer, and we’re seeing workers exercise their rights across the country by going on strike to demand better wages and working conditions,” said Representative Casar in a press release announcing the bill.
“Every union worker who is walking the picket line this summer needs to know that we have their back here in Washington,” said Fetterman.
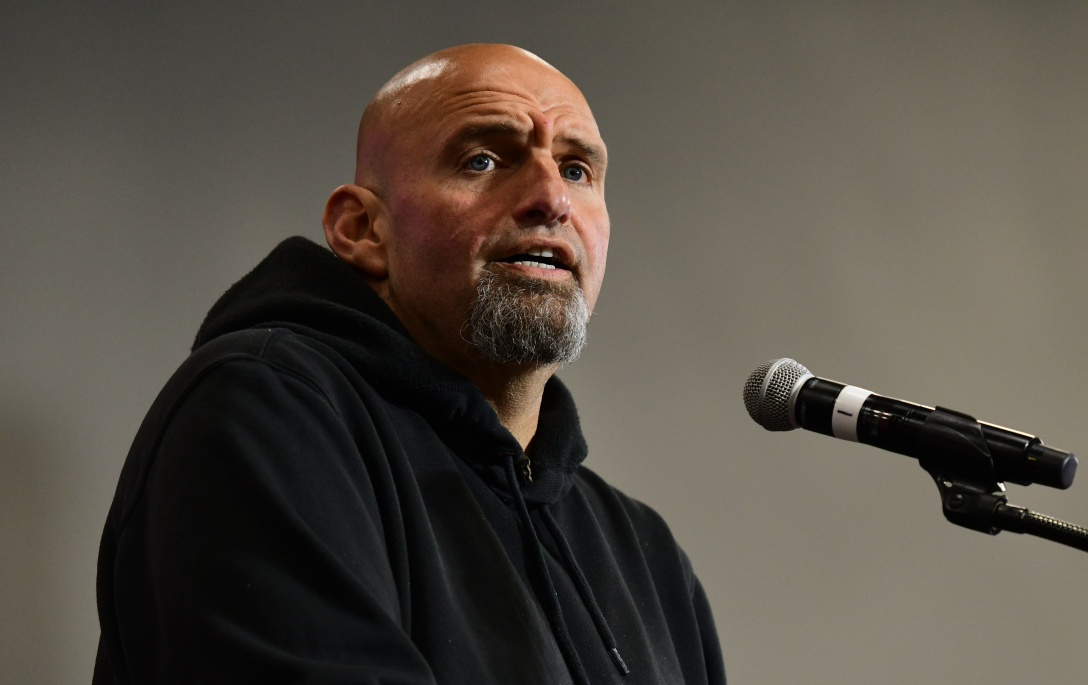

A number of bills have been introduced this year to support organizing and boost the resurgent labor movement, including the Striking and Locked Out Workers Healthcare Protection Act and the No Tax Breaks for Union Busting Act—but this is the first that’s aimed at providing greater food security for those on strike. Fetterman, who spearheaded the bill, is the chair of the Nutrition Subcommittee, which oversees SNAP.
“The right to strike is fundamental to the right to organize and unionize—but being forced to choose between feeding your family and protecting your labor rights isn’t a choice at all. With this bill John is fighting to make sure that hunger and starvation can’t be used as a weapon to break workers,” said Fetterman’s director of communications in an e-mail to The Nation.
Popular
“swipe left below to view more authors”Swipe →SNAP, which is administered by the US Department of Agriculture, offers food assistance to eligible households via monthly transfers to a dedicated card, which can then be used at certain food retailers. The country’s most important federal anti-hunger program, as of 2022 it assists 12 percent of the US population—or one in eight Americans—according to the Center of Budget and Policy Priorities.
Striking workers enjoyed SNAP benefits for nearly two decades, from the program’s launch in 1964 until 1981. In the summer of 1981—roughly two months before President Ronald Reagan broke the air traffic controllers’ (PATCO) strike—Congress passed an omnibus budget bill that included a provision barring striking workers from receiving SNAP. Unions and union members fought the measure in court, arguing that it was unconstitutional, but in 1988 the Supreme Court upheld the exclusion.
Bales views the Food Secure Strikers Act as part of a broader revival of the pre-Reagan labor movement, a process that he says will take a long time.
“Change is not sweeping, generally. It’s a game of inches,” he told The Nation. “So let’s move this forward a little bit this year, and a little bit next year and a little bit in the next Congress.”
More from The Nation

What Luigi Mangione and Daniel Penny Are Telling Us About America What Luigi Mangione and Daniel Penny Are Telling Us About America
When social structures corrode, as they are doing now, they trigger desperate deeds like Mangione’s, and rightist vigilantes like Penny.

Donald Trump Is the Authentic American Berserk Donald Trump Is the Authentic American Berserk
Far from being an alien interloper, the incoming president draws from homegrown authoritarianism.

Banning Trans Health Care Puts Young People at Risk of Harm Banning Trans Health Care Puts Young People at Risk of Harm
Contrary to what conservative lawmakers argue, the Supreme Court will increase risks by upholding state bans on gender-affirming care.

If Democrats Want to Reconnect With the Working Class, They Need to Start Listening to Unions If Democrats Want to Reconnect With the Working Class, They Need to Start Listening to Unions
The Democrats blew it with non-union workers in the 2024 election. Unions have a plan to get the party on message.