Maine Is in an Epic Battle Over Its Future
Voters could turn two private utilities into public goods. The corporations are fighting it tooth and nail.

There’s a moment in the ocean twice daily when it’s hard to read the flow of the water, and you can’t quite tell whether the current is going in or out. Mariners call this “slack tide.” While the name implies idleness, that’s not what’s really happening. There are big, opposing forces at work beneath the surface, and they are going to send the tide in one direction or the other very soon.
Politics in Maine has felt like a slack tide recently, especially around issues of climate and energy. Opposing forces of progress and regression are churning away at each other. The main fight centers on a November ballot measure that would turn the state’s private utilities public. If that happens, it would be a huge step toward dealing with the climate crisis, and a model for other states.
It’s easy for outsiders to forget about Maine, off by itself in the corner of the map. But it’s one of our most politically interesting states. Beyond its idiosyncratic electoral decisions—this is the state that once had the racist Republican former governor Paul LePage, the supposedly “moderate” Republican Senator Susan Collins, and the independent, Democratic-aligned Senator Angus King serving at the same time, though thankfully Mainers seem to have tired of LePage’s antics for good—it has a first-in-the-nation public financing scheme for candidates that lets a wide variety of people into the political pool, and a ranked-choice voting system for federal office that keeps third parties from being spoilers.
All those forces will be at play in November’s referendum, when voters must decide whether they want to turn the state’s two big private electric companies—Central Maine Power and Versant—into Pine Tree Power, a nonprofit, publicly run utility.
The two corporations sent $187 million in profits out of Maine last year—much of it to shareholders in such far-flung places as Qatar, Norway, and Canada. That’s serious money—and if it weren’t being sucked out of the state, the advocates of Pine Tree Power argue, Maine could lower rates by an average of $367 per household per year, which would mean shutting off fewer customers (nearly 10 percent of the state’s residential customers got disconnect notices last spring).
Moreover, with cheaper borrowing costs than the 10 or 12 percent return on equity that private companies demand, a public utility would be better prepared to build out the larger electric system that Maine will require as its residents give up oil furnaces and gas cars in the ongoing green transition. (The incumbent utilities are so ambivalent about renewables that Central Maine Power had to pay a $700,000 settlement for slow-walking the solar transition.) “We believe [utilities are] a direct way of targeting the fossil fuel industry,” Candice Fortin, the US campaigns manager for the climate group 350.org (which I helped found), explained recently. “Returning power to the people and looking for big fights is where we can best show solutions and also resist the fossil fuel infrastructure.”
Mainers care about climate change. The Gulf of Maine—the heart of the state’s fishing industry, and also much of its identity—is warming faster than almost any body of water on the planet. But that concern could be drowned in the nor’easter of commercials and mailings that the utilities are producing. As of this writing, they’re outspending public power advocates 32 to 1 and have dropped $27 million into the kitty—an extraordinary sum in a state with less than 1.5 million residents. (Though considering the aforementioned millions in profits they extracted from the state, confusing Maine voters is worth a good deal of money to them.) They’ve hired the Obama veterans who run Left Hook Strategy, as well as the Global Strategy Group, which last year tried to help Amazon crush a union drive at a Staten Island warehouse. The utilities have also created front groups like Maine Affordable Energy, whose executive director, Willy Ritch, said he didn’t think Mainers wanted “out-of-state politicians” telling them what to do; reporters pointed out that his group had taken $18 million in out-of-state money to oppose the referendum.
Bernie Sanders has been helping the Pine Tree campaign. “Power belongs in the hands of the people, not greedy corporations,” he declared.
The endless onslaught of anti-public-power TV ads may carry the day, but there’s not much else on the ballot, so turnout may be low, and there’s no question that the Pine Tree Power advocates are committed, disciplined, and creative.
There are also signs that the tide may have begun to turn decisively on climate issues in Maine. In July, the Legislature passed a law that should ease the way for a large-scale build-out of offshore wind power in the state’s Atlantic waters. Maine has enough wind to supply far more than its own needs; if it ends up selling power to other East Coast states, “the workers who are constructing these could be building a turbine or two every month for the next 30, 40, 50 years,” said Jack Shapiro, the climate and clean energy director of the Natural Resources Council of Maine.
But passing the law was no sure thing; offshore wind power has been stymied in the state in the past, largely because of opposition from fisheries interests worried that the turbines might interfere with fish stocks. And since the Maine Lobstering Union is affiliated with the state AFL-CIO, that was enough to keep organized labor on the sidelines.
Beginning in January, though, members of Maine’s labor community began meeting with fisheries groups, arguing that the gusher of money in the Inflation Reduction Act made it in the best interests of everyone to strike a deal. Fishermen wanted the wind turbines pushed farther offshore and the number of power cables minimized; with some of those elements in place, and with union wages guaranteed, the state AFL-CIO agreed to sign off on the plan.
Popular
“swipe left below to view more authors”Swipe →Unions representing the building trades have often been foes of environmentalists, but that dynamic may be changing elsewhere, too. In states such as Illinois, New York, Rhode Island, and Texas, climate activists and unions have begun negotiating over similar kinds of pacts.
Still, the status quo bias of labor unions sometimes can’t be overcome: The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers—and hence the Maine AFL—is siding with the bosses in opposing Pine Tree Power on the grounds that if workers were classed as public employees, they might lose the right to strike. Advocates for the public utility insist they’ve included language in the proposal that requires the elected board to contract out to a private operator, allowing the union to maintain that right.
As I said, slack tide. But slack tide never lasts more than a moment. Soon it’s flowing hard one way or the other. And Maine has the highest tides in the Lower 48.
More from The Nation

This Solar Panel Kills Fascists This Solar Panel Kills Fascists
New York’s Build Public Renewables Act will reduce carbon in the atmosphere, combat inequality, and help workers. It might also defeat Trumpism.
Global Burning Global Burning
The oil industry denies climate change, opposes regulations, and significantly contributes to the environmental crisis.
The “Worst COP” Concludes With a “Heartbreaking” Climate-Finance Deal The “Worst COP” Concludes With a “Heartbreaking” Climate-Finance Deal
Activists say the climate agreement effectively signed away the 1.5-degree Celsius target—”our only real chance to safeguard humanity’s future.”
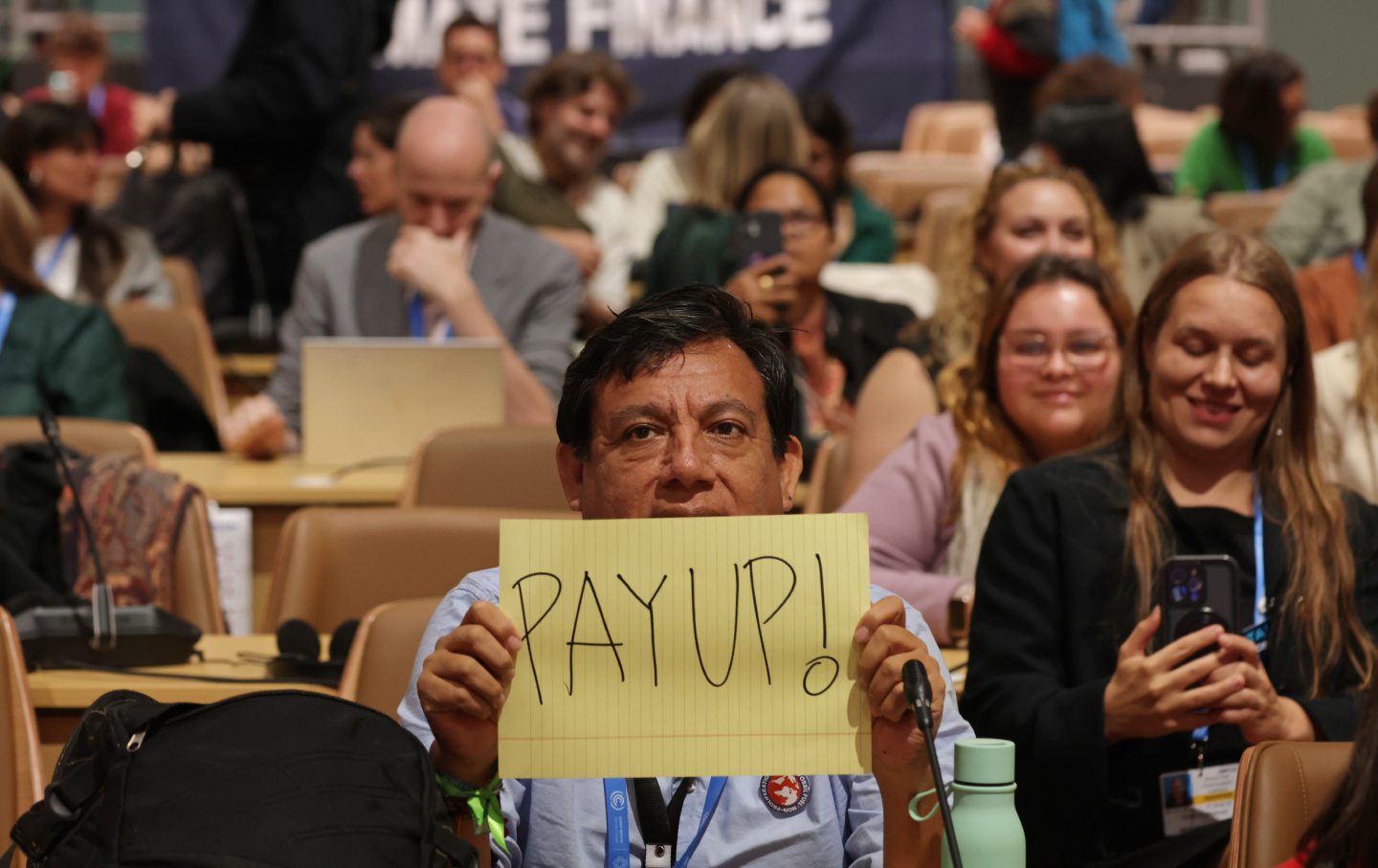

Rich Countries Must Pay Up or Humanity Will Pay the Price Rich Countries Must Pay Up or Humanity Will Pay the Price
The climate activist Lidy Nacpil says the climate bill owed to developing nations is in the “trillions, not billions.”

Climate Change Is the Real National Security Threat Climate Change Is the Real National Security Threat
In the wake of Hurricanes Helene and Milton, it’s clear we’re defending against the wrong perils.

Acting on Climate Change? Acting on Climate Change?
The opportunity is melting away.


