Climate Change Has Upended Kenya’s Agricultural Economy
As the region faces unprecedented flooding, farmers are struggling to make ends meet.
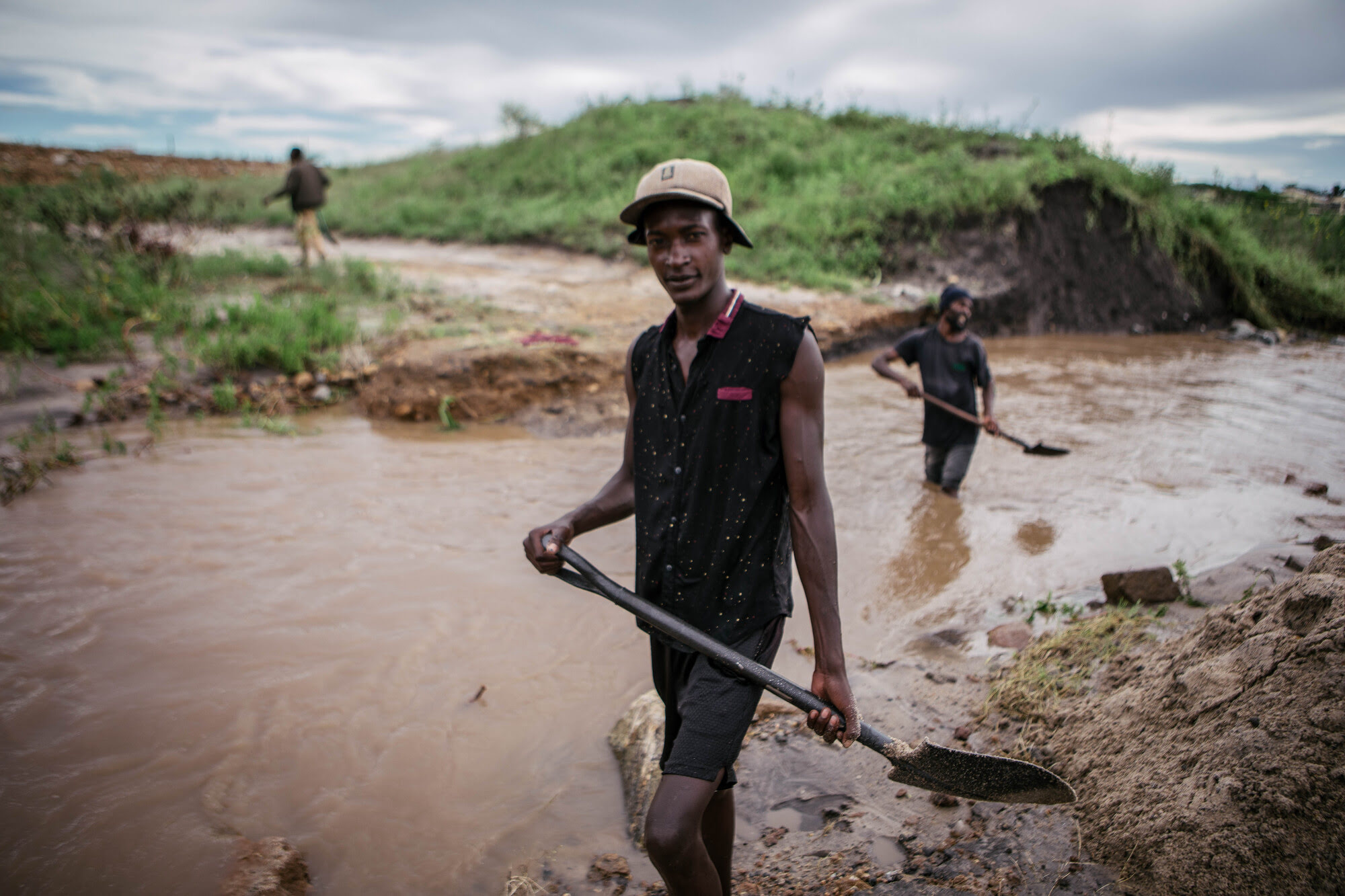

Every year, it’s typical in East Africa for the autumn to come with a short rainy season from October to December. But the rain in this region has gotten progressively worse, with last season’s downpour displacing more than half a million people and killing at least 174 people. This year, the UN says that 210 people have died in Kenya because of the catastrophic flooding.
Researchers found that the heavy and tumultuous rainfall in 2023 was about two times what it would have been without human-caused climate change. While a natural climate cycle known as the Indian Ocean Dipole has also contributed to the uptick in rainfall, scientists from the World Weather Attribution say the extreme flooding is the result of man-made environmental neglect.

On top of killing hundreds and displacing thousands, the extreme weather in Eastern Africa has also been particularly cataclysmic for those who rely on agricultural work to make ends meet.
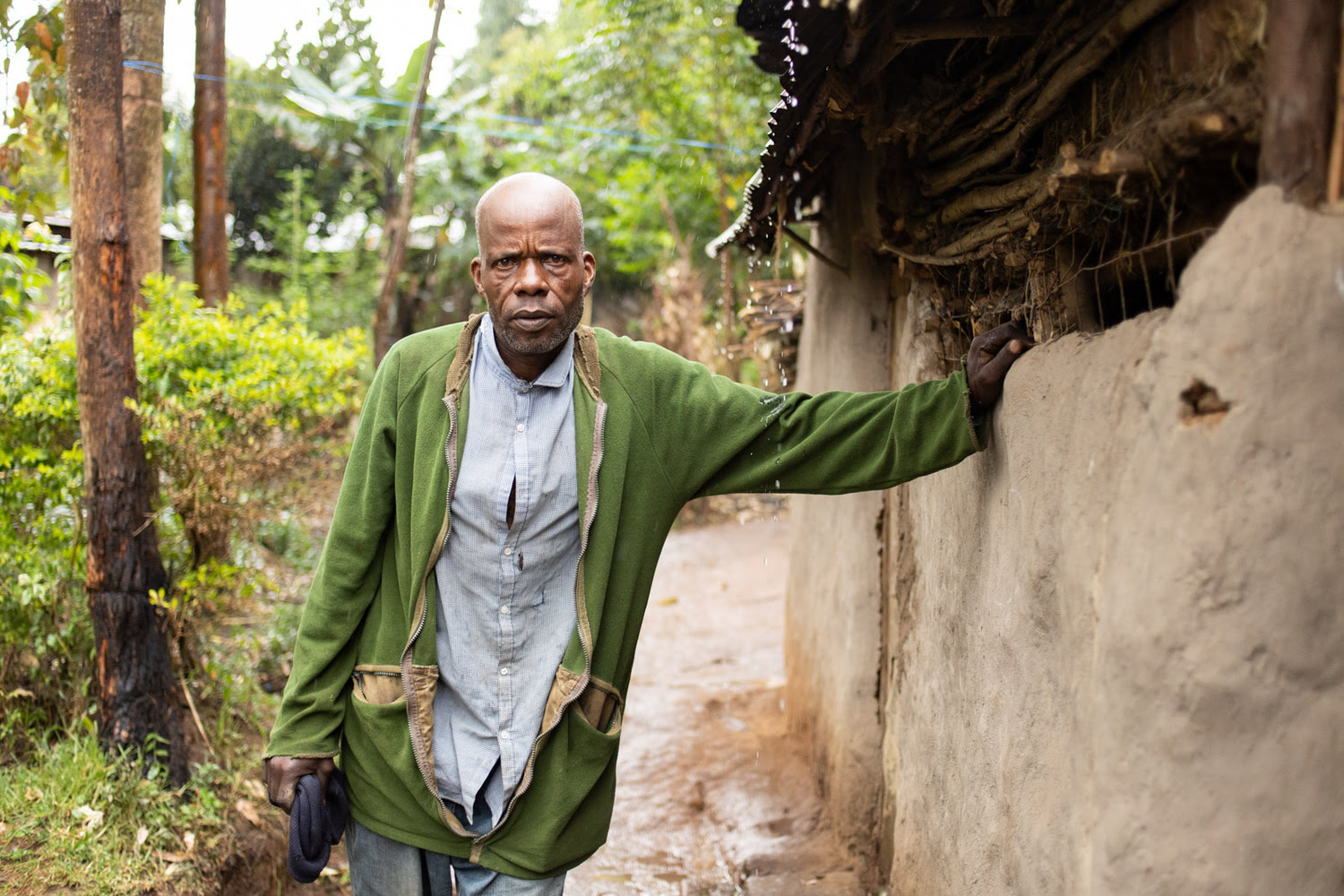
“Since October last year ‘til now, there’s [been] no farming work,” says Elkana Wanyama. Along with nine of their children, Elkana and his wife Rose live hand to mouth, depending mostly on casual labor.

In Kenya, agriculture employs more than 75 percent of the workforce, but in Kitale, the “breadbasket of Kenya,” an even greater percentage of people rely on casual employment from the agricultural sector.
Because of flooding on their small plot of land, Elkana and Rose can no longer plant corn, a staple crop that could feed their family. They’ve started planting eucalyptus to help drain the excess water. Previously, when too much rain would come, even their home would flood.
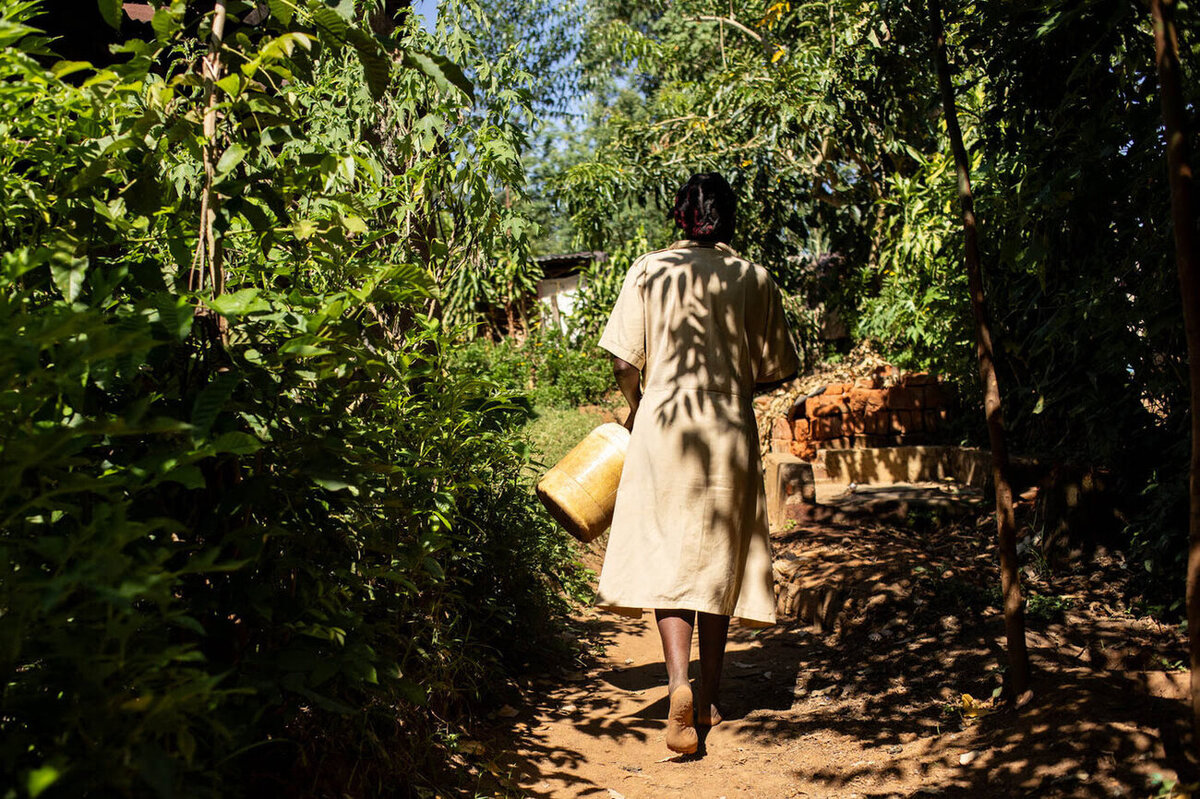

It used to be that December through February was the dry season. Rain would come in March, and farmers would plant corn accordingly. But these days, rain cycles are more and more unpredictable. Because of this, large-scale farmers have lower yields and are cutting employees, driving more people into poverty.
In Kenya, the majority of people in extreme poverty live in rural areas. The number of those living on less than $2.15 USD a day in rural regions is about 10.6 million, while 1.7 million people in extreme poverty live in urban areas.
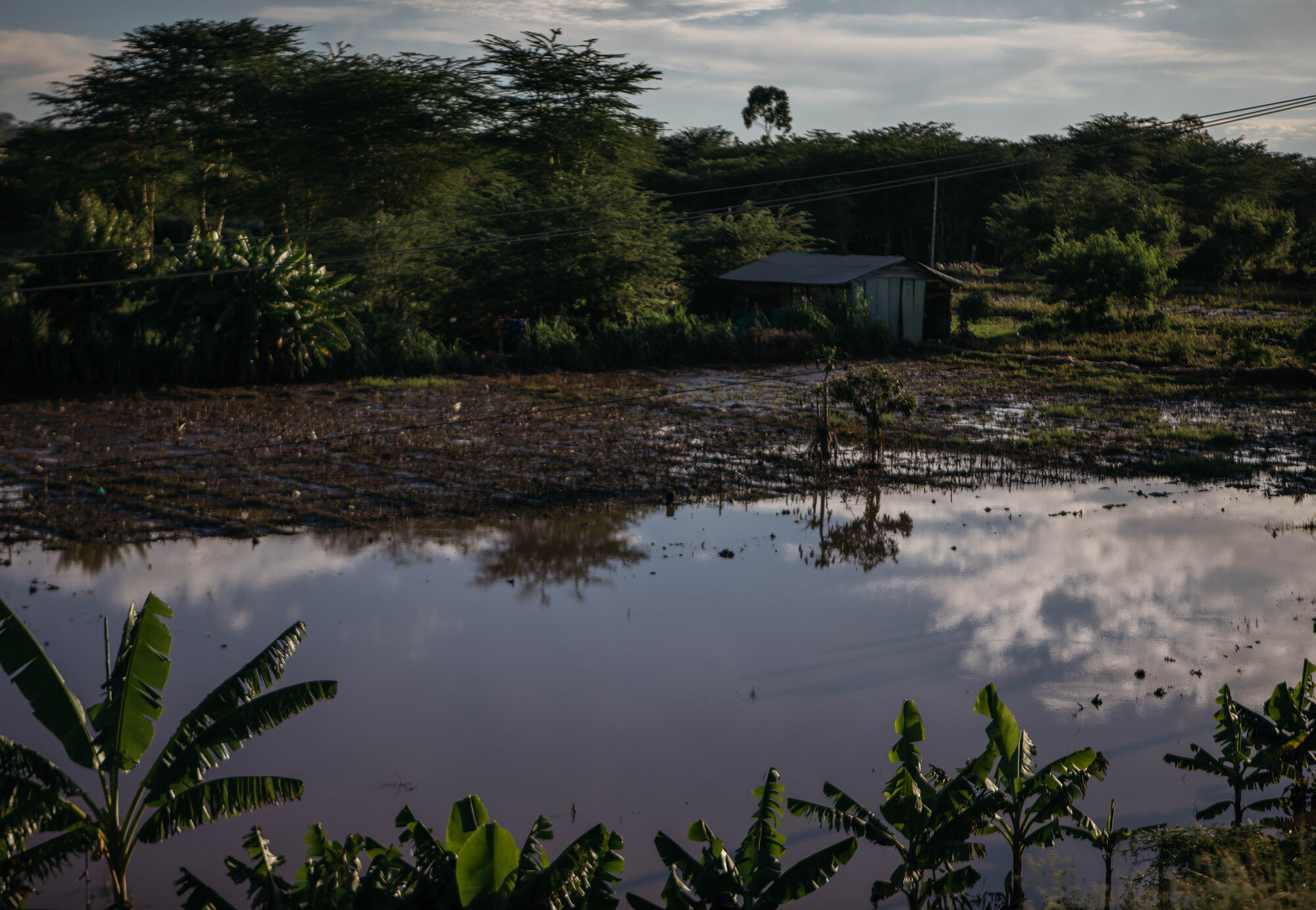

When floods do come, many families’ latrines overflow and sickness can spread through the neighborhood to those who don’t have money to go to the hospital. Locals share that cases of malaria are also increasing because mosquitos thrive in wet climates and those who cannot afford a mosquito net, a necessity in rural Kenya, are placed at further risk.
Pastor Stephen Churu says, “That’s when you find children dying. And that’s common for now and is really happening. Now [people] are asking, ‘Why don’t they find another means of disposing whatever they’re disposing that will not cause global warming?’ That is their great prayer that something can be done about it.”
With less crops being produced in Kitale, the cost of living and the price of food in all of Kenya has increased. Even neighboring countries depend on Kenya’s agricultural yield, making the lack of food an international crisis.





More from The Nation

What Comes After the Apocalypse? A Q&A With Joshua Oppenheimer What Comes After the Apocalypse? A Q&A With Joshua Oppenheimer
Oppenheimer’s latest film, The End, is a Golden Age, postapocalyptic musical crying out from the depths of the earth.

What Luigi Mangione and Daniel Penny Are Telling Us About America What Luigi Mangione and Daniel Penny Are Telling Us About America
When social structures corrode, as they are doing now, they trigger desperate deeds like Mangione’s, and rightist vigilantes like Penny.

Donald Trump Is the Authentic American Berserk Donald Trump Is the Authentic American Berserk
Far from being an alien interloper, the incoming president draws from homegrown authoritarianism.

Banning Trans Health Care Puts Young People at Risk of Harm Banning Trans Health Care Puts Young People at Risk of Harm
Contrary to what conservative lawmakers argue, the Supreme Court will increase risks by upholding state bans on gender-affirming care.